Intermittent Fasting for Weight Loss: Explore the Benefits, Foods And Process

Intermittent fasting (IF) is a prevalent health and fitness trend worldwide. Individuals adopt it to achieve weight loss, enhance their well-being, and streamline their daily routines. In addition, numerous studies have demonstrated its significant impact on the body and the mind, suggesting potential longevity benefits (1, 2). Here, we present the ultimate introductory guide to intermittent fasting for weight loss.
What Is Intermitted Fasting and How It Works?
While many diets focus on what you should eat, intermittent fasting revolves around when you eat. This approach involves restricting you’re eating to specific time windows. Research suggests that fasting for a set number of hours each day or consuming just one meal a couple of days a week may offer health benefits (3).
Intermittent fasting (IF) is a distinctive eating pattern characterized by alternating periods of fasting and eating. Unlike traditional diets that focus on specific food choices, IF primarily emphasizes the timing of meals.
Therefore, it can be more accurately described as an eating pattern rather than a conventional diet. The best intermittent fasting for weight loss methods include daily 16-hour fasts or fasting for 24 hours twice a week.
Fasting has been ingrained in human evolution for ages. Early hunter-gatherer societies needed more convenience of supermarkets, refrigerators, and year-round food availability. As a result, there were times when they struggled to find sustenance.
As a result, humans have adapted to function effectively during extended periods without food. Occasional fasting aligns more naturally with our evolutionary heritage than the constant consumption of three to four (or more) meals each day.
How Exactly Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Intermittent fasting involves various approaches; all centered around selecting specific periods for eating and fasting. For example, one method is restricting eating to an eight-hour window each day and fasting for the remaining hours. Alternatively, one could eat only one meal daily on two selected weekly days.
When the body goes without food for an extended period, it depletes its sugar reserves and transitions into burning fat. He refers to this metabolic shift as “metabolic switching.”
Intermittent fasting deviates from the typical eating pattern of many people, who consume different meals and snacks during the day. When individuals eat three meals a day, along with snacks, without exercising, they rely on the calories from each meal for energy instead of tapping into their fat stores.
Intermittent fasting works by extending the duration during which the body utilizes the calories from the previous meal and initiates fat burning.
Fasting Schedules: What Do You Need To Know?
Here are some popular schedules for intermittent fasting that you need to know about.
- Time-restricted eating: Fasting for at least 12 hours daily and consuming all meals within the remaining hours. A well-known example is the 16/8 method, where you fast for 16 hours and have an 8-hour eating window to fit in multiple meals.
- The 5:2 diet: With this approach, you usually eat five days a week and limit your calorie intake to 500-600 calories on the remaining two days.
- Alternate-day fasting: As the name suggests, in this schedule for intermittent fasting, you fast every other day following this pattern.
- Eat, Stop, Eat: This method includes fasting 24 hours once or twice weekly.
- The Warrior Diet: One of the earliest intermittent fasting diets, it involves consuming small amounts of raw fruits and vegetables during the day and having one large meal at night.
The Potential Benefits and Risks of Adopting Intermittent Fasting
Numerous studies have examined intermittent fasting in animals and humans, revealing its potential for significant benefits in weight management and overall body and brain health (2, 4). There is even evidence suggesting it could extend lifespan (1). So let’s explore the critical health advantages of intermittent fasting:
- Losing Weight: Weight loss is a prominent benefit of intermittent fasting. By implementing the IF methods, individuals can experience a significant reduction in weight and a reduction in belly fat, all without the need for calorie counting or calorie restriction.
Research studies have provided evidence supporting the effectiveness of intermittent fasting for weight loss (5). It allows individuals to achieve a caloric deficit without explicitly focusing on reducing their overall caloric intake. This is primarily attributed to the time-restricted eating patterns that intermittent fasting promotes.
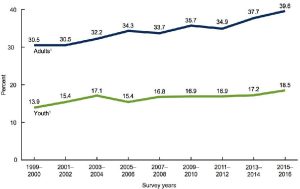
- Insulin Resistance: One notable benefit of intermittent fasting is its ability to decrease insulin resistance. This can reduce blood sugar levels by approximately 3-6% and a significant drop in fasting insulin levels by 20-31% (1). By improving insulin sensitivity, intermittent fasting offers potential protection against type 2 diabetes. Here is a graph explaining the effects of intermittent fasting on the insulin sensitivity of young people and adults.
Source: https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/9b90aac6f81937ffeb9f0fe5a9f91f8be28718b5/3-Figure1-1.png
- Inflammation: Studies have indicated that intermittent fasting for weight loss may contribute to a decrease in markers associated with inflammation, which is a significant contributor to various chronic diseases (6). Reducing inflammation markers can positively impact overall health and help mitigate the risk of developing chronic conditions.
- Heart Health: Intermittent fasting has demonstrated the potential to promote heart health by targeting several risk factors associated with cardiovascular disease. Studies have indicated intermittent fasting can reduce “bad” LDL cholesterol, blood triglycerides, inflammatory markers, blood sugar, and insulin resistance. These risk factors are known to contribute to the development of heart disease, and by addressing them, intermittent fasting shows promise in improving heart health (7).
- Cancer: Animal studies have suggested a potential role for intermittent fasting in cancer prevention. These studies have shown that intermittent fasting may have the ability to inhibit the growth and spread of cancer cells (8). Furthermore, intermittent fasting has been found to enhance the effectiveness of specific cancer treatments while reducing the side effects of chemotherapy (9). Although more research is needed to fully understand the impact of intermittent fasting on cancer prevention and treatment in humans, these preliminary findings are encouraging.
- Brain Health: Intermittent fasting has shown promising effects on brain health. It has been found to increase the production of a brain hormone called BDNF (brain-derived neurotrophic factor). BDNF plays a crucial role in promoting the growth and maintenance of nerve cells in the brain. By stimulating the production of BDNF, intermittent fasting may support the growth of new nerve cells, enhance brain plasticity, and improve cognitive function (10). Furthermore, intermittent fasting has been suggested to have potential protective effects against neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease. (11).
- Anti-aging: The concept of intermittent fasting and its potential anti-aging effects have gained attention in scientific research. Studies conducted on rats have shown that intermittent fasting can extend lifespan. In these studies, fasted rats increased their average lifespan by 36% to 83%. While translating these findings to humans requires further investigation, these results highlight the intriguing potential of intermittent fasting in promoting longevity and slowing down the aging process (12, 13).
Are There Any Risks to Intermittent Fasting?
It is quite common to experience some side effects when you first start with intermittent fasting. To keep you aware, we are mentioning some of these side effects.
- Hunger: Intermittent fasting can initially increase hunger but may subside over time. A 2022 study with 34 participants compared the 5:2 diet and calorie restriction with resistance training. After 12 weeks, both groups had low hunger levels and mostly adhered to their plans (14). In another study, 112 obese adults followed either a modified 5:2 diet or calorie restriction for a year. Both groups achieved similar weight loss and heart health benefits, but those on the 5:2 diet felt hungrier, on average (15).
- Headaches: Fasting can increase the likelihood of headaches, especially for those fasting for more than 16 hours and prone to headaches. Factors like caffeine withdrawal, dehydration, low blood sugar, and lack of sleep may contribute. Managing caffeine intake, staying hydrated, and maintaining good sleep habits can help alleviate fasting headaches.
- Fatigue and Mood Swings: Reduced fuel intake during fasting can lead to tiredness, difficulty concentrating, irritability, and aggression. Some studies suggest intermittent fasting can improve mental health and fatigue (16), but listening to your body and finding what works best for you is essential.
- Dehydration: Fasting can cause loss of salt and water, leading to dehydration. Early signs include dizziness, fatigue, and headaches. Increasing water intake and monitoring urine color can help prevent dehydration.
- Sleep Issues: Adjusting to intermittent fasting may initially disrupt sleep due to changes in meal times and circadian rhythm. However, some studies indicate that intermittent fasting may improve sleep quality in the long run (17).
- Malnutrition: Intermittent fasting affects meal timing, not food choices. Prolonged fasting increases the risk of inadequate nutrient intake. Symptoms of malnutrition include unintentional weight loss, feeling cold, tiredness or weakness, frequent illnesses, difficulty concentrating, and mood changes. Ensuring a balanced diet during eating periods is vital to prevent malnutrition.
Is Intermittent Fasting A Recommended Strategy For Losing Weight?
Intermittent fasting (IF) has gained popularity as a strategy for weight loss. While it may be effective for some individuals, whether it is a recommended strategy for losing weight depends on various factors and individual preferences. For instance, in 2005, a study revealed that intermittent fasting positively impacted insulin sensitivity in men while it hurt blood sugar control in women (18).
Anecdotal reports also suggest that intermittent fasting for women led to a pause in their menstrual cycle. Therefore, women should exercise caution when considering intermittent fasting as a dietary strategy.
However, it’s important to note that weight loss ultimately comes down to achieving a sustained calorie deficit, regardless of the specific diet strategy used. IF may help some individuals reduce their calorie intake and promote adherence to a structured eating pattern.
Before starting the intermittent fasting diet and weight loss plan, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian who can provide personalized recommendations based on your specific needs, health status, and preferences. In addition, they can help determine if intermittent fasting suits you and guide you through the process to ensure it is done safely and effectively.

Come on in for free!
Read, learn and become a better version of yourself by getting great trends on nutrition and wellness straight to your inbox.
The Best Foods to Eat During Intermittent Fasting
During intermittent fasting, consuming nutrient-dense foods that provide sustained energy and promote satiety is important. Here are some of the best foods to eat during intermittent fasting:
- Lean proteins: Chicken, turkey, fish, tofu, and eggs are excellent sources of protein that can help keep you feeling full and support muscle maintenance.
- Fiber-rich vegetables: Leafy greens, broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, and other non-starchy vegetables are low in calories and high in fiber, aiding digestion and providing essential nutrients.
- Healthy fats: Avocado, olive oil, nuts, and seeds can help promote satiety and provide essential fatty acids.
- Whole grains: Quinoa, brown rice, oats, and whole wheat products are complex carbohydrates that release energy slowly and help sustain you throughout the fasting period.
- Low-sugar fruits: Berries, apples, and citrus fruits are lower in sugar and packed with vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
Intermittent Fasting with Keto: Is It a Good Combination?
Combining intermittent fasting with keto can be an option for breaking through a weight loss journey or improving results. However, it’s important to note that there is limited scientific research on this approach, and its effectiveness for weight loss has yet to be proven. While it may seem logical, the lack of research suggests that you should carefully consider before adopting this eating approach.
Conclusion
Intermittent fasting for weight loss is a popular fasting method people use worldwide. This is a good idea if you want to lose weight rapidly and without many adverse side effects. However, contacting a healthcare professional to get the full scope of intermittent fasting is always recommended.
Is intermittent fasting healthy?
Intermittent fasting can be a healthy approach for some individuals. Research suggests it may aid weight loss, improve metabolic health, and offer other potential benefits. However, it’s important to consider individual factors, such as existing health conditions, before starting any new dietary regimen. Consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian is recommended to determine if intermittent fasting is appropriate.
How do I start intermittent fasting?
Choose a fasting schedule that suits your lifestyle to start intermittent fasting for weight loss. Common methods include the 16/8 method (fasting for 16 hours and eating within an 8-hour window), the 5:2 method (eating normally for five days and restricting calorie intake for two non-consecutive days), or alternate-day fasting. Gradually increase fasting durations and allow your body to adapt. Stay hydrated, consume nutrient-rich meals during eating windows, and listen to your body’s signals.
How much weight can you lose in a month with intermittent fasting?
Weight loss results with intermittent fasting can vary widely depending on factors such as individual metabolism, calorie intake, exercise, and adherence to the fasting protocol. It is possible to lose several pounds within a month with intermittent fasting, but the amount will vary for each person. Therefore, it’s important to prioritize sustainable weight loss practices and focus on overall health to have good intermittent fasting before and after results.
What is the best schedule for intermittent fasting?
The best schedule for intermittent fasting depends on personal preference and lifestyle. The 16/8 method is popular, as it is relatively easy to implement. This involves fasting for 16 hours and eating within an 8-hour window. However, some people succeed with longer fasting periods or alternative fasting methods like the 5:2 or alternate-day fasting. Experiment with different schedules to find what works best for your body and fits seamlessly into your routine.
What are the best foods to break intermittent fasting?
When breaking an intermittent fast, it’s advisable to prioritize nutrient-dense foods that provide sustained energy and nourishment. Opt for whole foods like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats. Avoid highly processed and sugary foods that may cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. Gradually reintroduce food and listen to your body’s hunger and fullness cues. Remember to hydrate adequately throughout the fasting period and during eating windows.
How long does intermittent fasting last?
The duration of intermittent fasting can vary depending on the method you choose to follow. For example, the 16/8 process involves fasting for 16 hours and eating within an 8-hour window. Other methods, such as alternate-day fasting, may involve more extended fasting periods. It’s essential to find a fasting duration that is sustainable and comfortable for you. Start with a shorter fasting window and gradually increase the duration as your body adapts.
Is eating fast food for 12 or 16 hours better?
Regarding intermittent fasting, a fasting period of 16 hours is generally recommended for most methods. Extending the fasting window to 16 hours is more beneficial than limiting it to 12 hours when aiming for metabolic and health benefits. However, listening to your body and choosing a suitable fasting duration is essential. Maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet during the eating window is also important to support overall health.