Have you ever felt off balance?
Like your body is malfunctioning on a micro level?
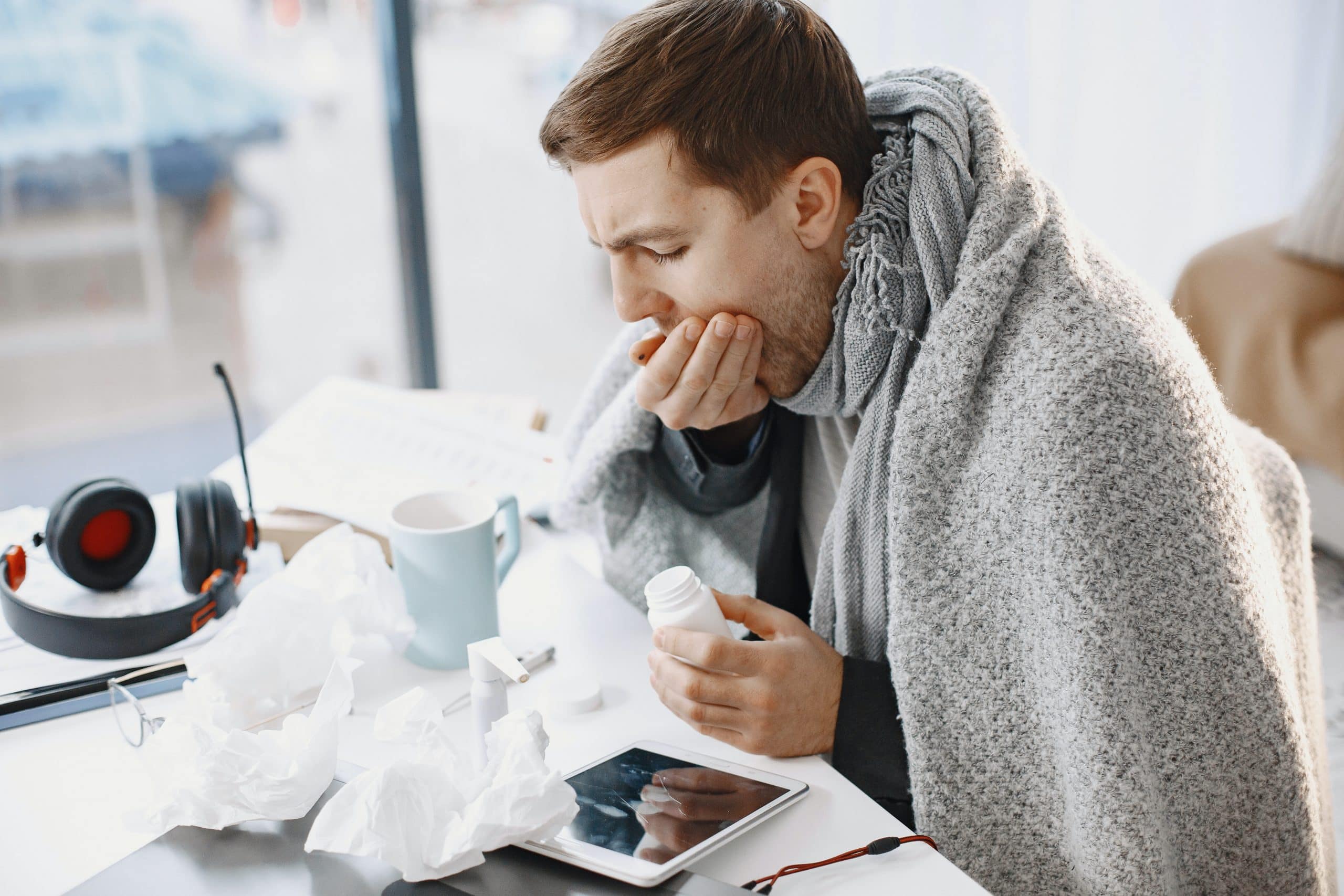
You are always tired, you are having poor digestion and muscle weakness and you can’t figure out why?
A very probable reason may be the deficiency of micronutrients for example chlorine. From the acid in your stomach to the fluid in your body stay in a state of balance because of this electrolyte. About 8.8% of people in intensive care units had low chloride levels, according to a study.
What is Hypochloremia?
Human beings have a blood chloride level of 96 and 106 milliequivalents per litre of blood (mEq/L). If it falls below this level you start to show signs of hypochloremia which is caused by low blood chloride levels.
Symptoms of low chloride
The body always tells you when something is wrong with it. The important point is to understand what your body is trying to tell you. If you have lost a lot of water due to recent food poisoning or heavy workout or you are feeling exhausted despite sleeping well you might be having a deficiency of chlorine in your system. Let’s check out the symptoms of low chloride.
- Fever – Fever is often a sign of systemic imbalance.
- Difficulty Breathing – Metabolic alkalosis may often be accompanied by troubled breathing.
- Confusion – chloride maintains nerve conduction therefore chloride deficiency may cause confusion.
- Swelling – Chloride maintains fluid levels, an imbalance of which may cause water retention and swelling.
- Metabolic alkalosis – a chloride deficiency is a life-threatening condition called alkalosis.
Causes of Hypochloremia
The chief source of chloride in our diets is the humble table salt. Given how salt is ubiquitous in our diets, a nutritional deficiency of chloride is quite a rare occurrence. Things get interesting when we look at how chloride is absorbed and distributed in our bodies.
Chloride is chiefly absorbed in the gut and cleared by the kidneys. The kidneys play a major role in maintaining chloride homeostasis. Any derangements in these two systems lead to low chloride levels in the blood.
Some Conditions and Diseases that may lead to Hypochloremia are as follows-:
- Diarrhoea– Diarrhoea may be triggered by a number of bacteria, protozoa and other microbes. It leads to watery and frequent stool. However, water and faecal matter are not the only things removed from the body during diarrhoea. Copious amounts of minerals are also lost and chloride is among them.
- Vomiting- As with diarrhoea, vomiting may be triggered by GI infections, emotional upheaval, trauma and injury to the brain. Chloride is lost with water and other particles while vomiting following the same mechanism as diarrhoea.
- Excessive sweating– Heavy exercise, stress, and obesity may lead to excessive sweating. While it may not seem like much, our body may lose deceptively large amounts of water and minerals due to sweating. This is what gives sweat a salty taste and why most sports drinks come packed with electrolytes.
- Kidney problems– As previously mentioned, the renal system plays a major role in regulating chloride levels in the blood. Any acute or chronic insult to the kidneys will lead to derangements in chloride levels.
- Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone excretion (SIADH)- This is a relatively rare condition in which the body produces too much antidiuretic hormone. This hormone is responsible for maintaining the water balance in the body and this syndrome may lead to hypochloraemia.
- Lung diseases- Lung diseases may also lead to low chloride levels due to a disbalance in pH.
- Cancer treatment- Chemotherapy often affects our systems, especially kidneys. Although the signs show up much later, kidney impairment may result in excessive loss of electrolytes leading to hypochloremia.
How is Hypochloremia Diagnosed?
One of the best ways to diagnose the condition is to visit your doctor if you have lost quite a lot of fluid in the past few days.
So you might think, how much is too much?
Follow the 4/24 rule. If you have 4 episodes of diarrhoea in 24 hrs it’s time you see your doctor in order to avoid hypochloremia. The doctor might prescribe the following tests to detect hypochloremia.
Blood test –There isn’t an individual test for chlorine. An electrolyte panel is a blood test that measures chloride, bicarbonate, potassium, and sodium. It measures the quantity of chlorine in your blood and helps detect hypochloremia.
Urine test – Chlorine levels in the blood are regulated by the kidney. So chlorine is also excreted in the urine. Sometimes certain drugs may cause excessive filtering out of Chlorine may be indicative of hypochloremia.
Can it be Prevented?
Here are a few ways that may help you prevent further loss of chlorine.
- Avoid unregulated use of diuretics or laxatives- Excessive use of either of them may result in further fluid and electrolyte loss.
- Avoid consumption of beverages- Beverages containing caffeine and alcohol further dehydrate you so if you want to replenish your lost fluid and electrolytes, cut them off like your toxic relative.
- Medications- Watch out for medications like bicarbonates and corticosteroids that have a history of altering chlorine levels in your body.
How to Increase Chloride Levels
- Drink electrolytes- If you have lost a lot of water due to diarrhoea, vomiting or workout you should consume a good amount of water added with electrolytes to recharge and replenish. ORS is a readily available, simple and inexpensive remedy. Alternatively, you may take 1 litre of boiled water, add six level teaspoons of sugar and half a level teaspoon of salt. Stir well to dissolve and drink at regular intervals. Another choice is a sports drink/ electrolyte drink (drinks with 6-7% carbohydrates per serving are the best for your overall health).
- Medication/ Supplements- If you have any systemic condition that causes hypochloremia, it’s recommended to take supplements under medical advice.
- Saline drip- If your chlorine levels are extremely low you may go for saline drip/ Intravenous saline solution to stabilise your electrolyte levels.
Conclusion
Chloride ions are among the most important electrolytes in the body. Chloride is involved in almost each and every cellular process. Fortunately, low levels of chloride are not very common in the general population but a downturn in chloride levels might well land you in the hospital if not addressed promptly. Being aware of the causes, symptoms and treatment will help you combat this condition swiftly and effectively.
FAQs
Here are a few frequently asked questions about hypochloremia –
How to increase chloride levels naturally?
Is a chloride level of 110 bad?
A chloride level above 110 mEq/L in critically ill septic shock patients is associated with elevated hospital mortality. Normal saline use during resuscitation should be administered cautiously to treat non-anion gap hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis.
Blood chloride levels are typically considered normal when they fall within the range of 98-107 mEq/L. A level of 110 mEq/L is considered excessive and can lead to severe health problems, such as hypertension and cardiovascular issues.